
WHAT’S IN A LEMON?
You probably think you already know everything about lemons, but let’s take it bit by bit, literally! Want to know what’s under (and inside of) that peel?
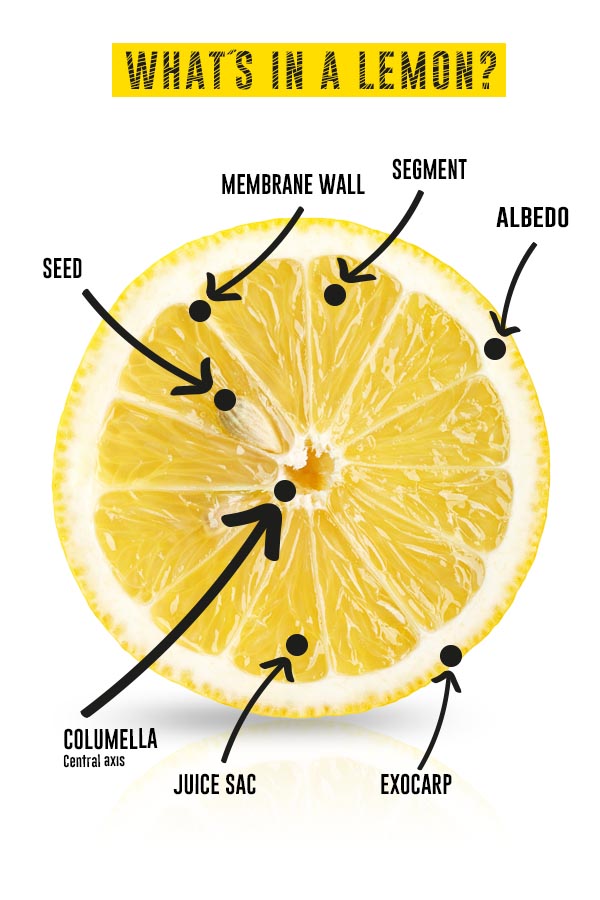
FLAVEDO (peel layer)
Ranging from green to bright yellow in color depending on ripeness, it contains numerous essential oil glands that are responsible for its aroma. These glands form an effective barrier against attacks by insects and microorganisms.
ALBEDO
The white, spongy inner layer of the fruit and the most important source of pectin and carbohydrates. Its thickness varies according to the variety and the ripeness of the fruit.
ENDOCARP (pulp)
The edible part, representing between 65% and 70% of the lemon’s weight. It is pale yellow in color. It is generally divided into segments that contain elongated cells where water, carbohydrates, and citric acid accumulate, known as the juice sacs. Each slice contains hundreds of sacs, and occasionally there may be a seed.
COLUMELA (central axis)
The central part of the lemon. Depending on the variety, it can be thicker or thinner.
Privacy Policy
Legal Notice
Cookies Policy




